Abstract
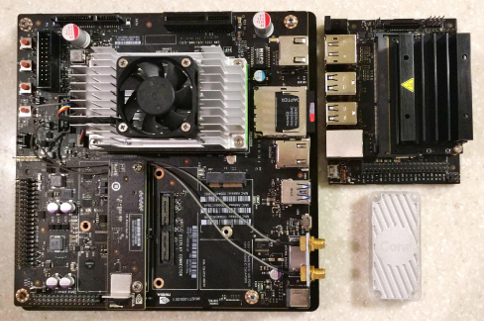
With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT), large amount of data are generated at edge devices with an unprecedented speed. In order to protect the privacy and security of big edge data, as well as reduce the communications cost, it is desirable to process the data locally at the edge devices. In this study, the inference performance of several popular pre-trained convolutional neural networks on three edge computing devices are evaluated. Specifically, MobileNetV1 & V2 and InceptionV3 models have been tested on NVIDIA Jetson TX2, Jetson Nano, and Google Edge TPU for image classification. Furthermore, various compression techniques including pruning, quantization, binarized neural network, and tensor decomposition are applied to reduce the model complexity. The results will provide a guidance for practitioners when deploying deep learning models on resource constrained edge devices for near real-time and on-site learning.