Abstract
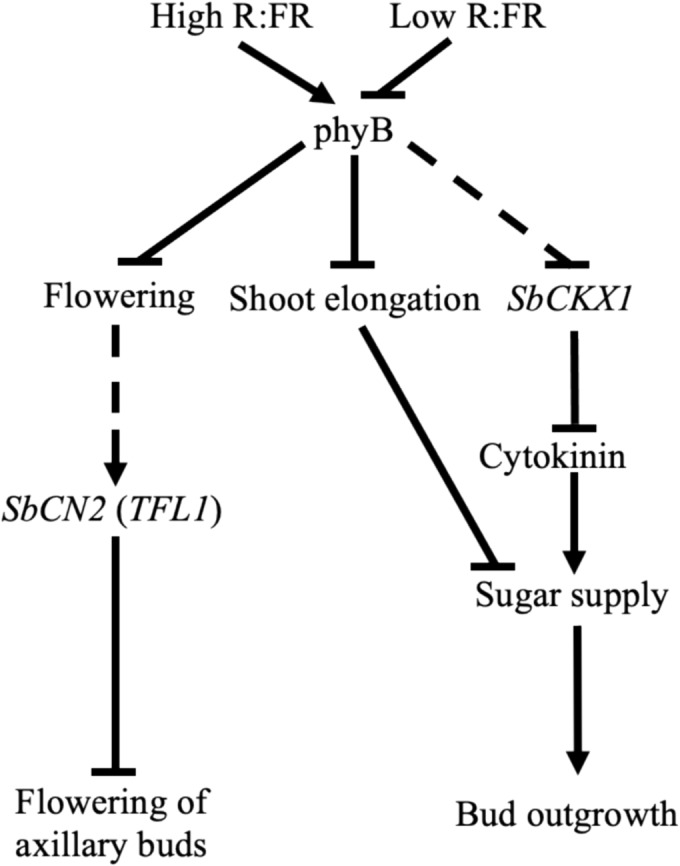
Shoot branches grow from axillary buds and play a crucial role in shaping shoot architecture and determining crop yield. Shade signals inactivate phytochrome B (phyB) and induce bud dormancy, thereby inhibiting shoot branching. Prior transcriptome profiling of axillary bud dormancy in a phyB-deficient mutant (58M, phyB-1) and bud outgrowth in wild-type (100M, PHYB) sorghum genotypes identified differential expression of genes associated with flowering, plant hormones, and sugars, including SbCN2, SbNCED3, SbCKX1, SbACO1, SbGA2ox1, and SbCwINVs. This study examined the expression of these genes during bud dormancy induced by shade and defoliation in 100M sorghum. The aim was to elucidate the molecular mechanisms activated by shade in axillary buds by comparing them with those activated by defoliation. The expression of marker genes for sugar levels suggests shade and defoliation reduce the sugar supply to the buds and induce bud dormancy. Intriguingly, both shade signals and defoliation downregulated SbNCED3, suggesting that ABA might not play a role in promoting axillary bud dormancy in sorghum. Whereas the cytokinin (CK) degrading gene SbCKX1 was upregulated solely by shade signals in the buds, the CK inducible genes SbCGA1 and SbCwINVs were downregulated during both shade- and defoliation-induced bud dormancy. This indicates a decrease in CK levels in the dormant buds. Shade signals dramatically upregulated SbCN2, an ortholog of the Arabidopsis TFL1 known for inhibiting flowering, whereas defoliation did not increase SbCN2 expression in the buds. Removing shade temporarily downregulated SbCN2 in dormant buds, further indicating its expression is not always correlated with bud dormancy. Because shade signals also trigger a systemic early flowering signal, SbCN2 might be activated to protect the buds from transitioning to flowering before growing into branches. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that shade signals activate two distinct molecular mechanisms in sorghum buds: one induces dormancy by reducing CK and sugars, whereas the other inhibits flowering by activating SbCN2. Given the agricultural significance of TFL1-like genes, the rapid regulation of SbCN2 by light signals in axillary buds revealed in this study warrants further investigation to explore its potential in crop improvement strategies.