Abstract
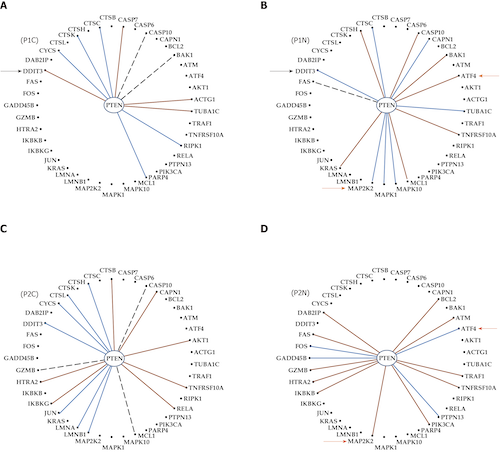
Every day, investigators find a new link between a form of cancer and a particular alteration in the sequence or/and expression level of a key gene, awarding this gene the title of “biomarker”. The clinician may choose from numerous available panels to assess the type of cancer based on the mutation or expression regulation (“transcriptomic signature”) of “driver” genes. However, cancer is not a “one- gene show” and, together with the alleged biomarker, hundreds other genes are found as mutated or/and regulated in cancer samples. Regardless of the platform, a well-designed transcriptomic study produces three independent features for each gene: Average expression level, expression variability and coordination with expression of each other gene. While the average expression level is used in all studies to identify what genes were up-/down-regulated or turn on/off, the other two features are unfairly ignored. We use all three features to quantify the transcriptomic change during the progression of the disease and recovery in response to a treatment. Data from our published microarray experiments on cancer nodules and surrounding normal tissue from surgically removed tumors prove that the transcriptomic topologies are not only different in histopathologically distinct regions of a tumor but also dynamic and unique for each human being. We show also that the most influential genes in cancer nodules [the Gene Master Regulators (GMRs)] are significantly less influential in the normal tissue. As such, “smart” manipulation of the cancer GMRs expression may selectively kill cancer cells with little consequences on the normal ones. Therefore, we strongly recommend a really personalized approach of cancer medicine and present the experimental procedure and the mathematical algorithm to identify the most legitimate targets (GMRs) for gene therapy.