Abstract
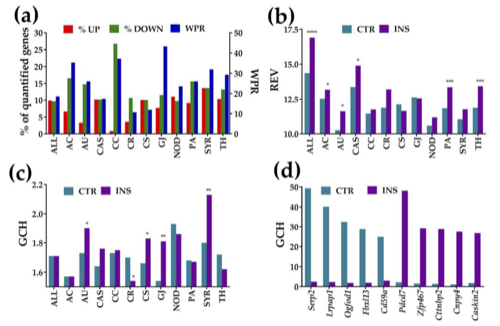
We profiled the transcriptomes of primary mouse cortical astrocytes cultured alone or co-cultured with immortalized precursor oligodendrocytes (Oli-neu cells). Filters between the cell types prevented formation of hetero-cellular gap junction channels but allowed for free exchange of the two culture media. We previously reported that major functional pathways in the Oli-neu cells are remodeled by the proximity of non-touching astrocytes and that astrocytes and oligodendrocytes form a panglial transcriptomic syncytium in the brain. Here, we present evidence that the astrocyte transcriptome likewise changes significantly in the proximity of non-touching Oli-neu cells. Our results indicate that the cellular environment strongly modulates the transcriptome of each cell type and that integration in a heterocellular tissue changes not only the expression profile but also the expression control and networking of the genes in each cell phenotype. The significant decrease of the overall transcription control suggests that in the co-culture astrocytes are closer to their normal conditions from the brain. The Oli-neu secretome regulates astrocyte genes known to modulate neuronal synaptic transmission and remodels calcium, chemokine, NOD-like receptor, PI3K-Akt, and thyroid hormone signaling, as well as actin-cytoskeleton, autophagy, cell cycle, and circadian rhythm pathways. Moreover, the co-culture significantly changes the gene hierarchy in the astrocytes.