Abstract
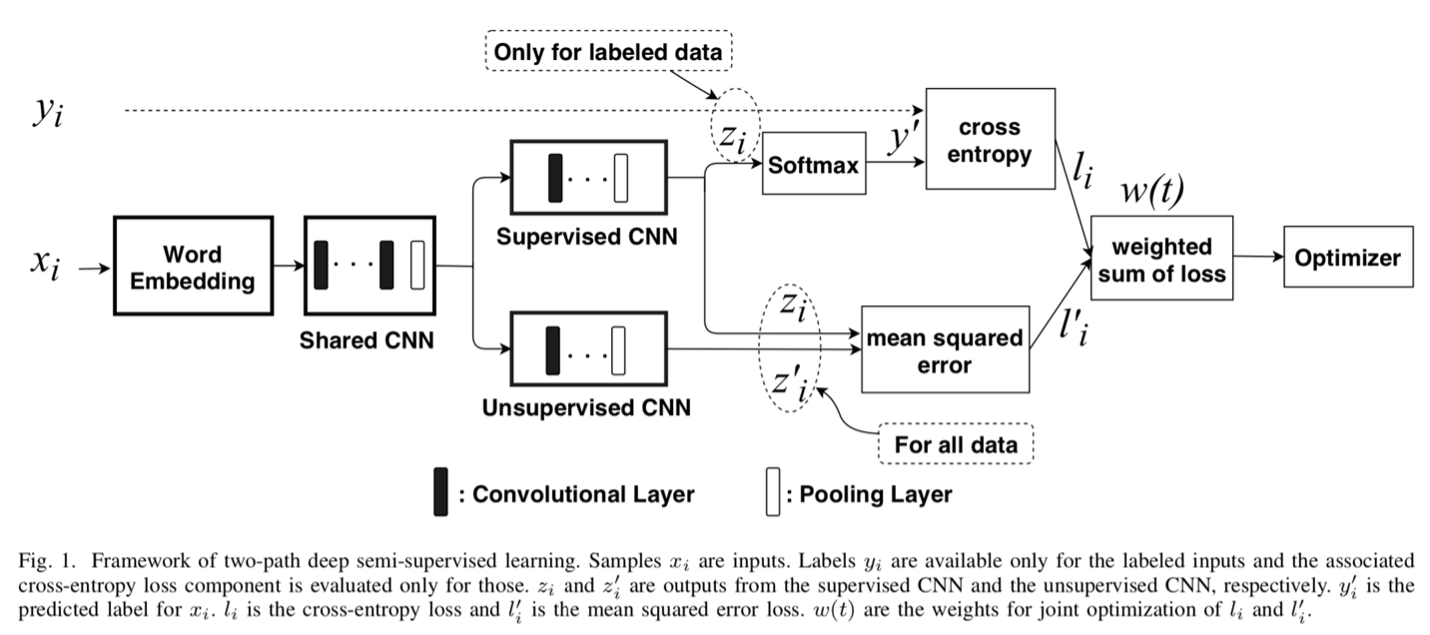
News in social media, such as Twitter, has been generated in high volume and speed. However, very few of them are labeled (as fake or true news) by professionals in near real time. In order to achieve timely detection of fake news in social media, a novel framework of two-path deep semisupervised learning (SSL) is proposed where one path is for supervised learning and the other is for unsupervised learning. The supervised learning path learns on the limited amount of labeled data, while the unsupervised learning path is able to learn on a huge amount of unlabeled data. Furthermore, these two paths implemented with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are jointly optimized to complete SSL. In addition, we build a shared CNN to extract the low-level features on both labeled data and unlabeled data to feed them into these two paths. To verify this framework, we implement a Word CNN-based SSL model and test it on two data sets: LIAR and PHEME. Experimental results demonstrate that the model built on the proposed framework can recognize fake news effectively with very few labeled data.