Abstract
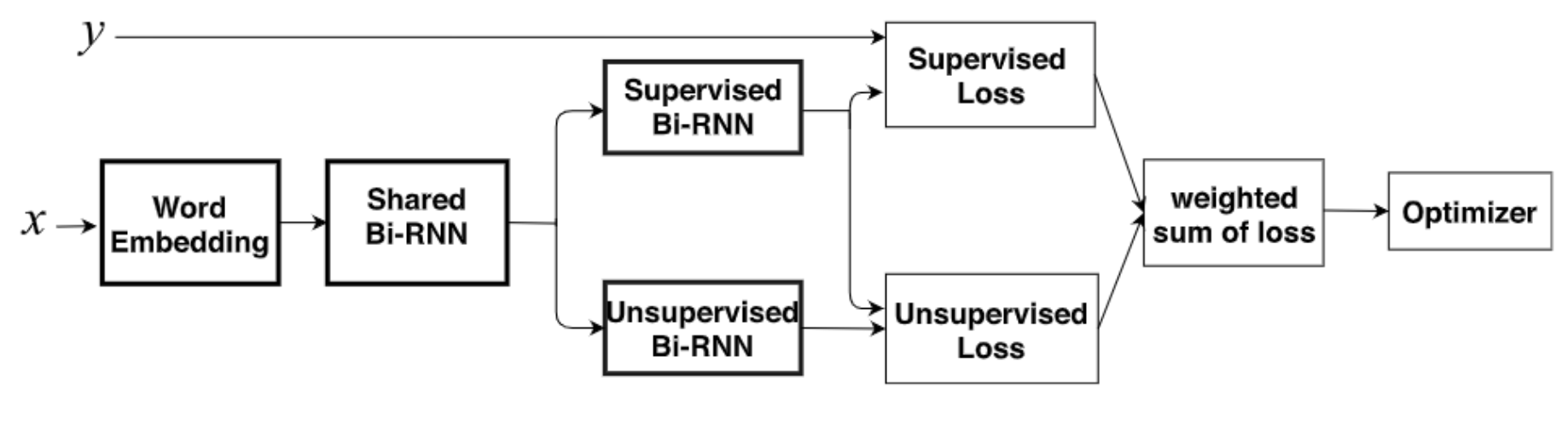
Misinformation refers to inaccurate information created to misguide the readers. It spreads on social platforms like Twitter with various presentations such as fake news and rumors that usually contain numbers, categorical information, texts, images, etc., which has become a global issue of cybersecurity. We propose a semi-supervised deep model based on bidirectional recurrent neural networks (Bi-RNN) to detect misinformation with limited labeled data and large unlabeled data. The proposed model consists of three components, namely, shared Bi-RNN, supervised Bi-RNN, and unsupervised Bi-RNN. Specifically, the shared Bi-RNN provides common features that input to the supervised Bi-RNN and unsupervised Bi-RNN, and they jointly optimize two losses, namely, cross-entropy loss and mean-square-error loss, using both labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data. We validate our proposed model by testing on two benchmark datasets of misinformation: LIAR and PHEME. It is observed that the proposed model is able to achieve promising performance even with very limited labeled data for training when compared to baselines with supervised deep learning.