Abstract
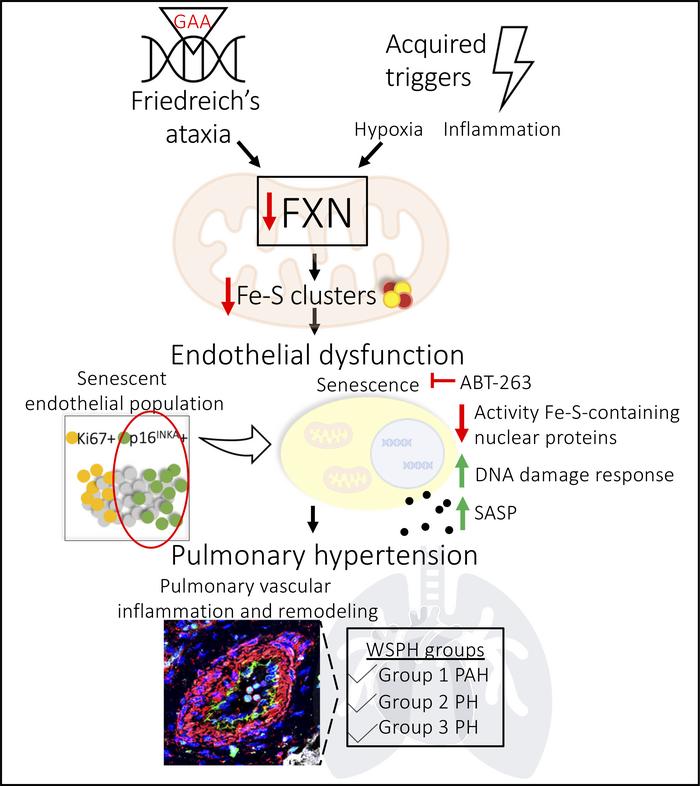
The dynamic regulation of endothelial pathophenotypes in pulmonary hypertension (PH) remains undefined. Cellular senescence is linked to PH with intracardiac shunts; however, its regulation across PH subtypes is unknown. Since endothelial deficiency of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters is pathogenic in PH, we hypothesized that a Fe-S biogenesis protein, frataxin (FXN), controls endothelial senescence. An endothelial subpopulation in rodent and patient lungs across PH subtypes exhibited reduced FXN and elevated senescence. In vitro, hypoxic and inflammatory FXN deficiency abrogated activity of endothelial Fe-S-containing polymerases, promoting replication stress, DNA damage response, and senescence. This was also observed in stem cell-derived endothelial cells from Friedreich’s ataxia (FRDA), a genetic disease of FXN deficiency, ataxia, and cardiomyopathy, often with PH. In vivo, FXN deficiency-dependent senescence drove vessel inflammation, remodeling, and PH, while pharmacologic removal of senescent cells in Fxn-deficient rodents ameliorated PH. These data offer a model of endothelial biology in PH, where FXN deficiency generates a senescent endothelial subpopulation, promoting vascular inflammatory and proliferative signals in other cells to drive disease. These findings also establish an endothelial etiology for PH in FRDA and left heart disease and support therapeutic development of senolytic drugs, reversing effects of Fe-S deficiency across PH subtypes.